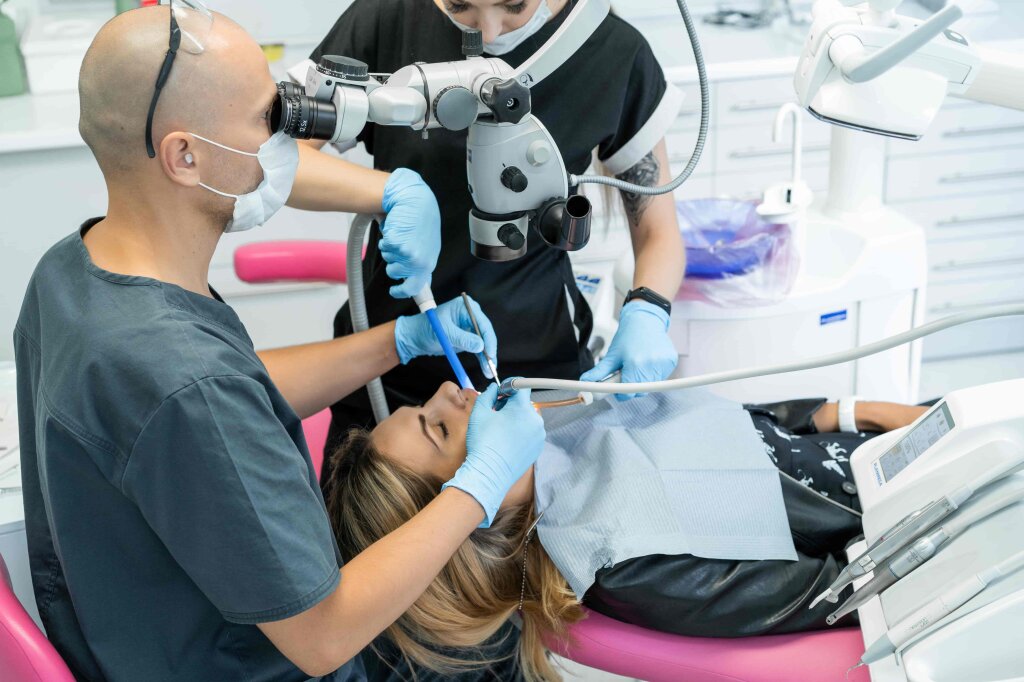
Gum diseases are a common health issue that causes inflammation and damage to the gums. These diseases, often asymptomatic in the early stages, can lead to severe consequences, including tooth loss, if left untreated. Knowing the symptoms and treatment methods of gum diseases is crucial for maintaining your oral health.
Symptoms of Gum Diseases
The symptoms of gum diseases typically start mildly and become more noticeable over time. Therefore, recognizing changes in your gum health early on is the most effective way to prevent the disease from progressing.
Gum Bleeding: The most common symptom of gum diseases is bleeding gums when brushing or flossing. This is a sign of gum inflammation and usually indicates the early stage of gum disease known as gingivitis.
Swelling and Redness of the Gums: Healthy gums should be pink and firm. However, in gum diseases, the gums swell, become red, and tender. This is a sign of inflammation.
Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath (halitosis) can also be a symptom of gum disease. This results from bacterial infections in the gum tissue and doesn’t go away even with proper oral hygiene.
Gum Recession: As gum disease progresses, the gums may recede. As the gums pull back, the roots of the teeth become exposed, making the teeth appear longer. This increases tooth sensitivity and the risk of tooth loss.
Loose Teeth: The progression of gum disease can damage the bone and connective tissue that support the teeth, leading to loose teeth or even tooth loss.
Treatment Methods for Gum Diseases
The treatment of gum diseases varies depending on the stage and severity of the disease. Gum diseases detected at an early stage can be controlled with simpler treatment methods, while more advanced cases may require more extensive interventions.
Professional Teeth Cleaning: The first step in treating gum diseases is a professional teeth cleaning performed by a dentist. During this process, plaque and tartar deposits on the teeth are removed. Plaque is one of the main causes of gum disease and needs to be cleaned regularly.
Root Planing (Curettage): In more advanced stages of gum disease, it may be necessary to clean the root surfaces of the teeth. This procedure, known as root planing (curettage), helps remove bacterial infection in the gum pockets and allows the gums to reattach to the teeth.
Antibiotic Therapy: Bacterial infections that cause gum disease can be treated with antibiotics. Antibiotics can be taken orally or applied directly to the gum pockets. This treatment helps control inflammation and prevent the spread of infection.
Laser Treatment: One of the modern methods used in the treatment of gum diseases is laser treatment. The laser precisely cleans the infected gum tissue and also accelerates the healing process of the gums. Laser treatment is often preferred as a minimally invasive method.
Gum Surgery: In advanced cases of gum disease, surgical intervention may be required. These interventions include reshaping the gum tissue, gum grafts, and bone grafts. These surgical procedures help reconstruct the supporting structures of the teeth and restore gum health.
Regular Oral Hygiene: One of the most important steps in treating gum disease is maintaining daily oral hygiene. Regular brushing, flossing, and using antiseptic mouth rinses help prevent the progression of gum disease.
Ways to Prevent Gum Diseases
To prevent gum diseases, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene and visit the dentist regularly. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, use dental floss, and visit your dentist regularly to prevent plaque buildup. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding smoking play a significant role in protecting your gum health.
Gum diseases can lead to serious health problems if not detected early. Knowing the symptoms of gum disease and consulting your dentist as soon as you notice them is the most effective way to protect your oral health. Professional treatment methods and regular oral care are crucial in preventing and treating gum diseases.