What is Gum Inflammation?
Gum inflammation, also known as gingivitis, occurs due to the accumulation of food particles and other debris between the teeth, which over time leads to the formation of dental plaque, tartar, and calculus. If personal oral hygiene is neglected, this condition can progress to bone loss and even tooth loss if left untreated.
Symptoms of Gum Inflammation
Gum inflammation can severely affect oral health and presents with symptoms that should be recognized early. Here are the symptoms:
Receding Gums: The gum line pulls back, exposing the roots of the teeth.
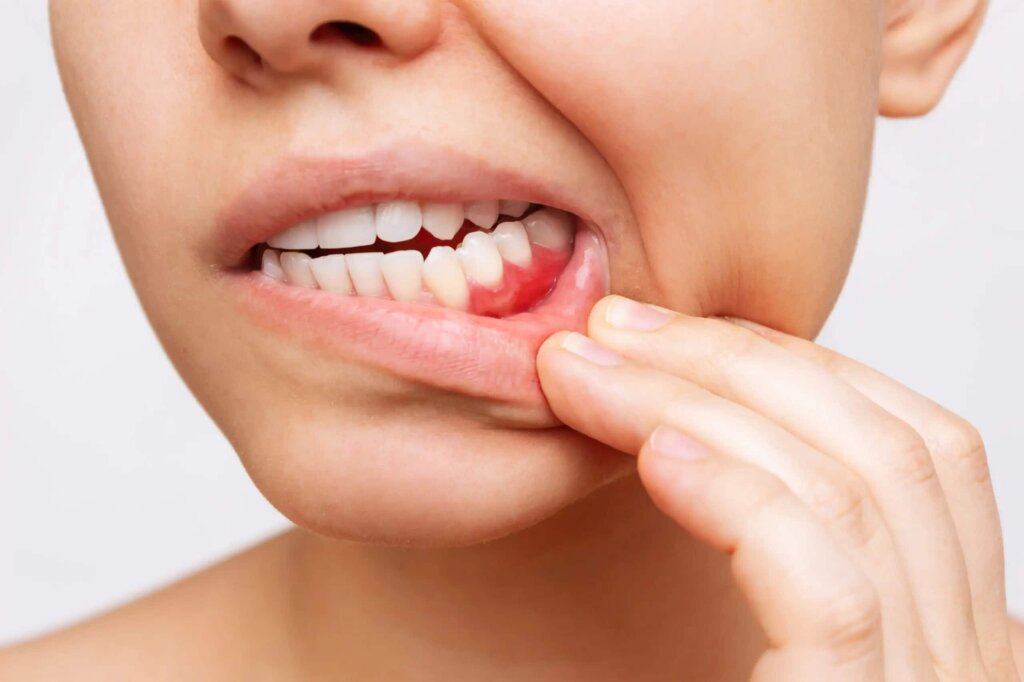
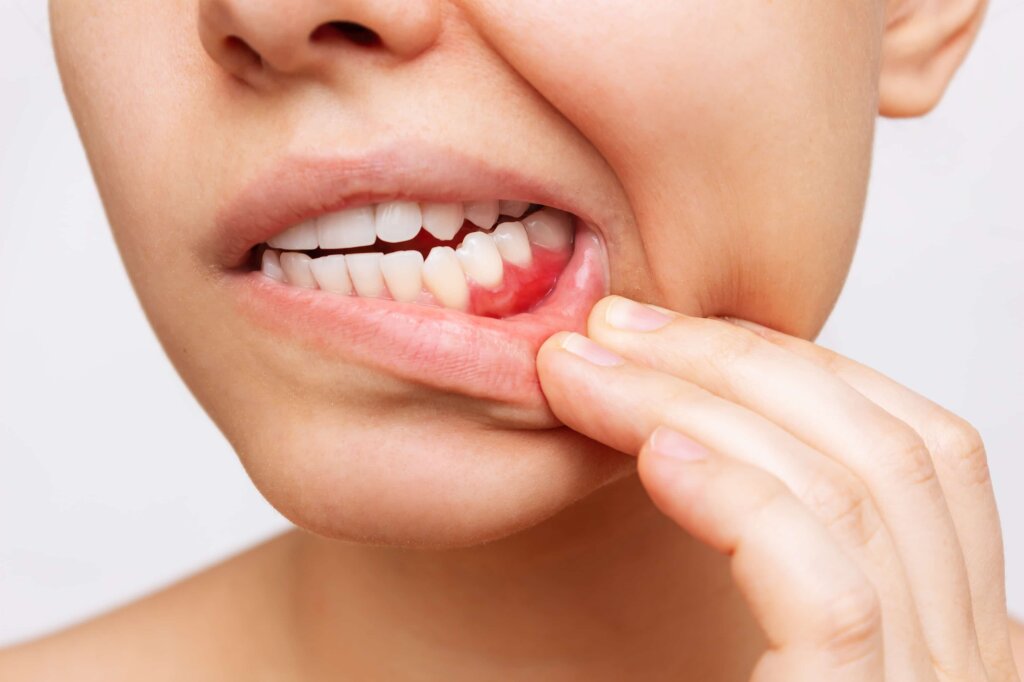
Bleeding During Brushing: Bleeding of the gums when brushing or flossing.
Redness and Swelling: Inflamed gums appear red and swollen.
Pain and Sensitivity: In advanced cases, gums may be painful to touch and sensitive to hot or cold temperatures.
Bad Breath: Gum inflammation can cause bad breath, which may disturb others during conversation.
Causes of Gum Inflammation
The primary cause of gum inflammation is inadequate cleaning of the teeth and plaque buildup. Plaque is a sticky, colorless layer of bacteria that forms on the teeth. Over time, plaque becomes tartar (calculus), which irritates the gums.
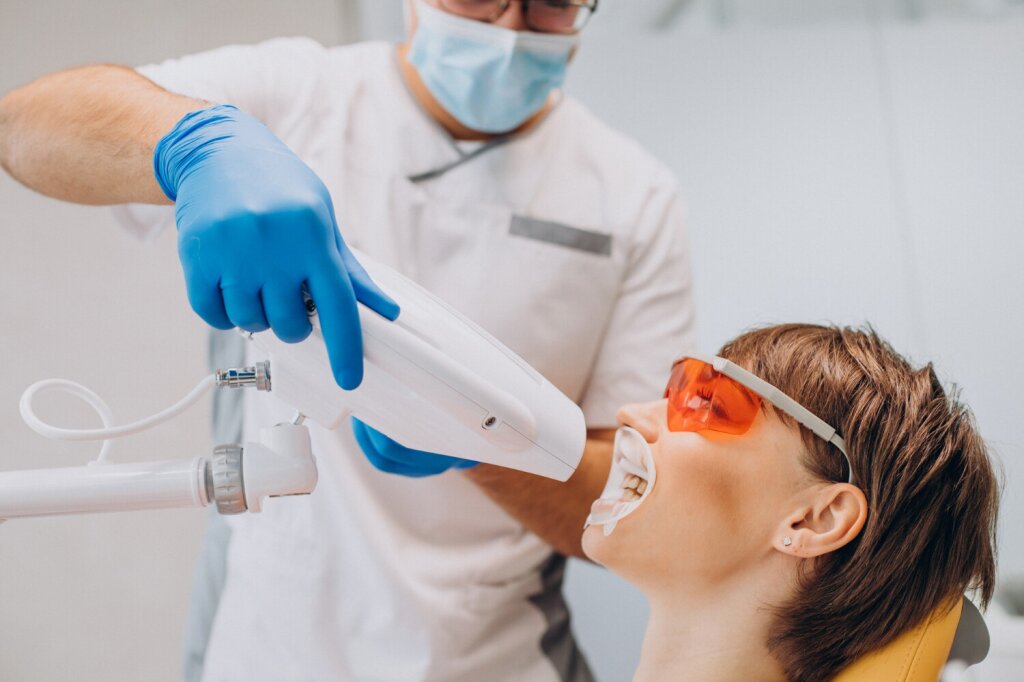
Treatment Methods for Gum Inflammation
Early diagnosis is crucial in treating gum inflammation. If untreated, gum disease can progress to periodontitis, increasing the risk of tooth loss. At Istanbul Dental Academy's Polyclinic in Maltepe Zümrütevler, our expert team uses various methods to treat gum inflammation:
Scaling and Root Planing: Removal of plaque and tartar from the teeth.
Flap Surgery: In advanced stages of gum disease, the gums are surgically lifted, the root surfaces are cleaned, and the gums are then repositioned.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can gum inflammation be prevented? Brush your teeth regularly, use floss, and rinse your mouth with mouthwash. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleaning are also important.
Is gum inflammation painful? Early-stage gum inflammation may not be painful. However, as the condition progresses, sensitivity and pain in the gums may occur.
What happens if gum inflammation is not treated? Untreated gum inflammation can progress to periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss. Serious issues such as bone loss and tooth mobility may also arise.
What foods should people with gum inflammation avoid? Individuals with gum inflammation should avoid hard and sticky foods and prefer soft, nutritious foods.
How is gum inflammation treated? Gum inflammation is treated with scaling, deep cleaning (root planing), and, if necessary, surgical intervention (flap surgery).